Category: Aviation Law


4.82.4 Transponder Code – Loss of Communications

4.82.6 Transponder Code – Unlawful Interference

4.80.4 Notification of Incidents/Accidents.
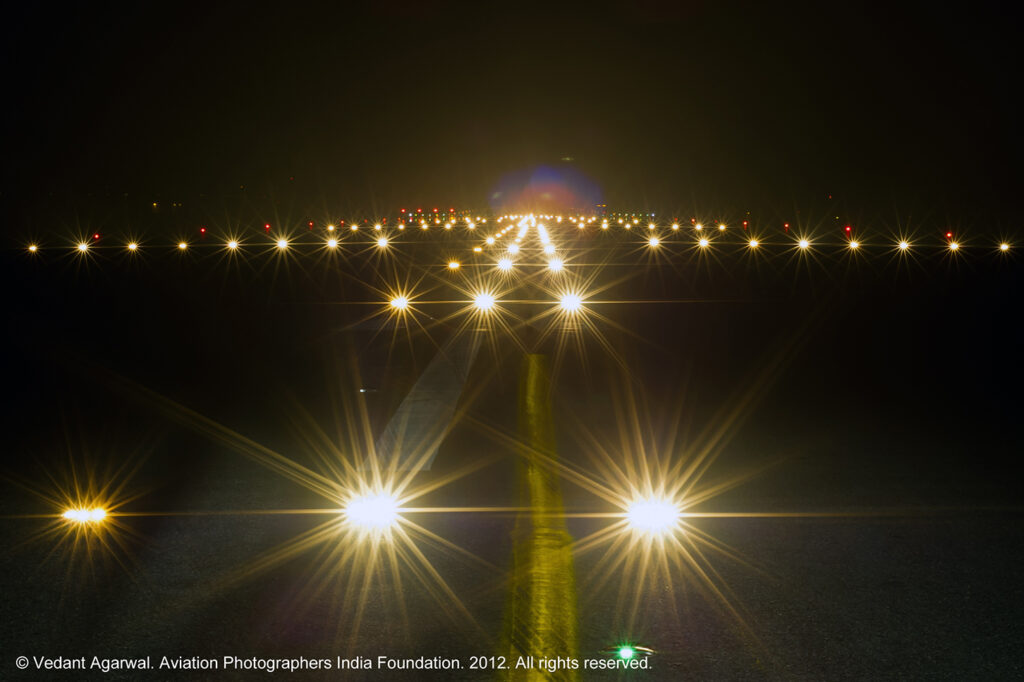
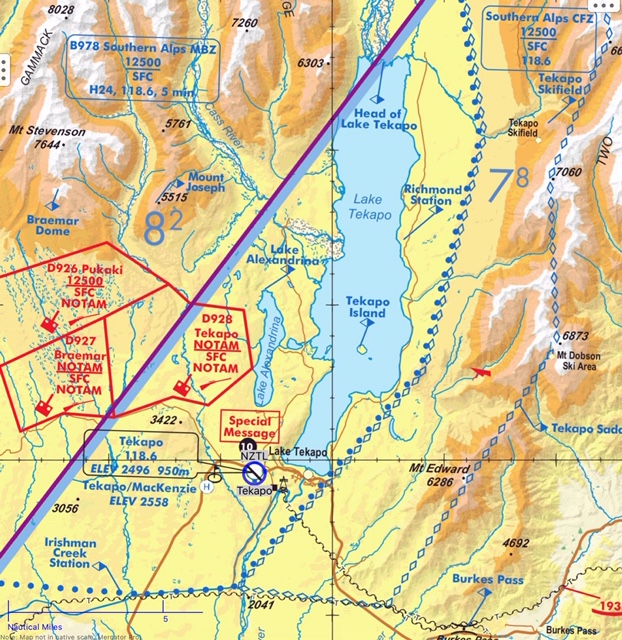
4.78 Aerodromes Lighting / Pilot Activated Lighting
4.66.2 Radar Services available to VFR flights.
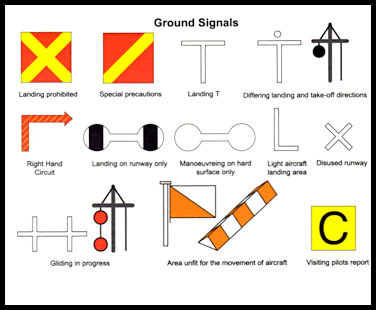
4.76.8 Meaning of the various Aerodrome Ground Signals.
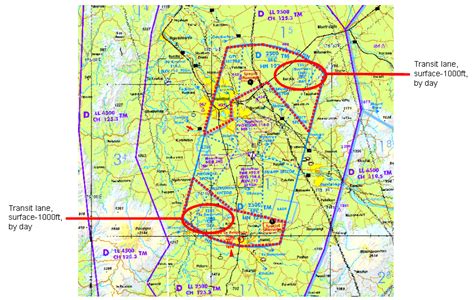
4.75.8 Flight in VFR Transit Lanes
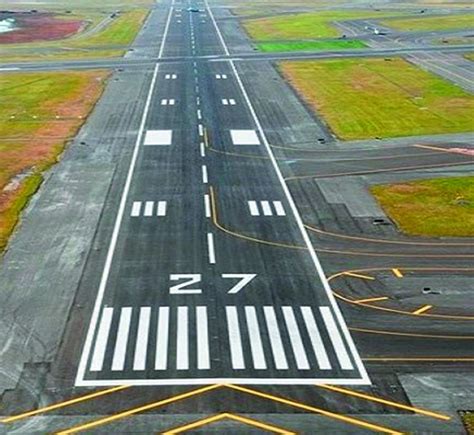

4.76.4 Method of Runway Designation